Many developers still believe Zoho is limited to low-code tools like Zoho Creator. But that’s no longer the case. With Zoho’s official Java SDK, backend developers can now build robust, enterprise-grade applications using Java Spring Boot and directly integrate with Zoho CRM. This powerful combination allows full control over logic, data sync, and API handling—delivering high performance and flexibility for production deployments. At Codroid Labs, we specialize in merging these technologies to create scalable, secure, and maintainable systems for modern enterprises.
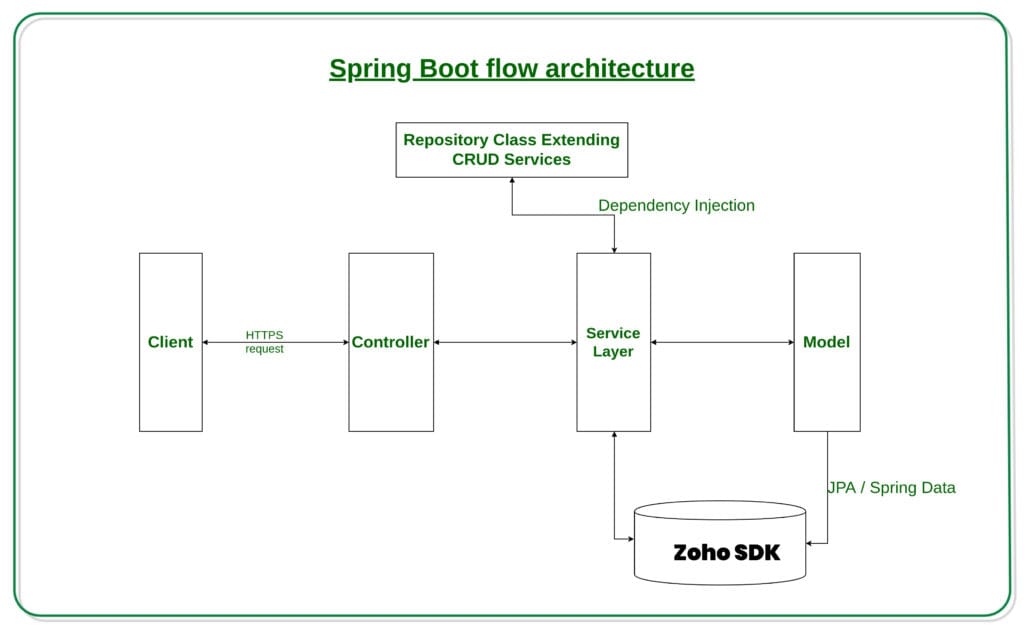
Spring Boot Architecture Overview
Spring Boot provides a clean and scalable architecture for integrating external SDKs like Zoho CRM. Below is a visual representation of the flow:
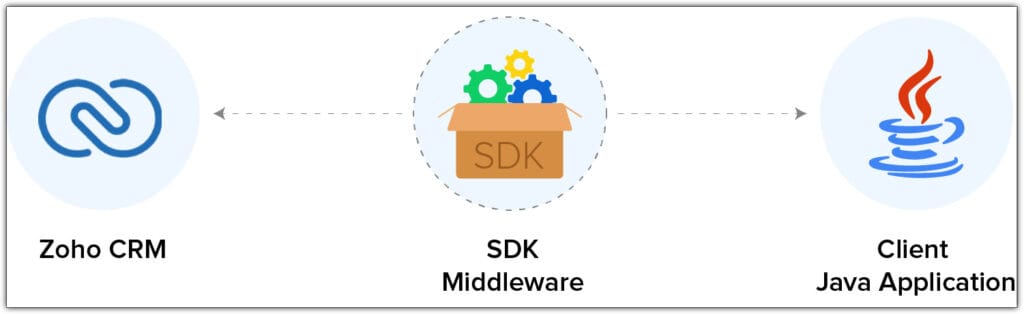
SDK Middleware Explained
The Zoho CRM SDK acts as middleware between your Spring Boot application and the Zoho CRM platform. It handles authentication, token management, and structured API calls seamlessly.
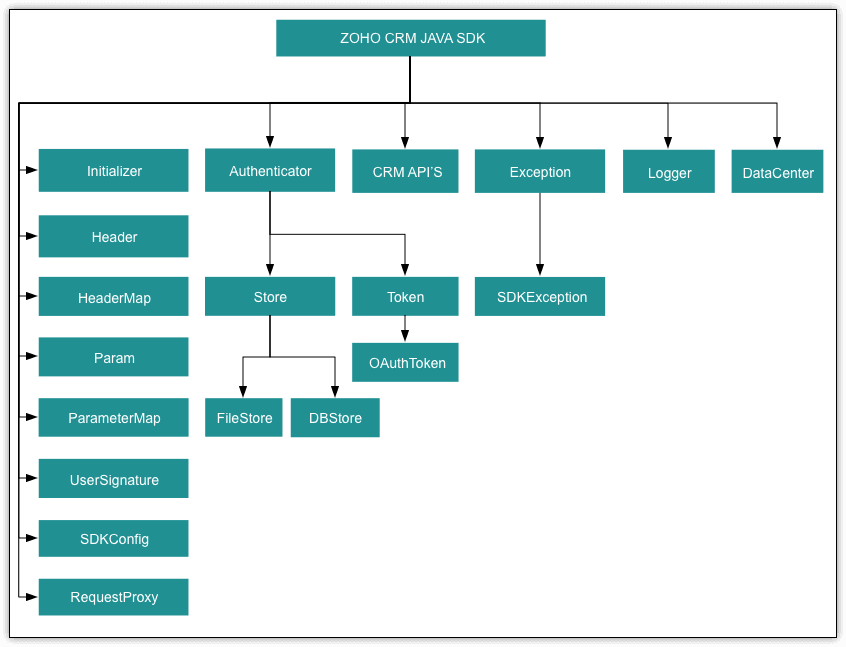
SDK Class Hierarchy Overview
Zoho provides a comprehensive Java SDK that comes with essential classes and utilities for authenticating, logging, token storage, and CRM API handling.
Implementation Guide: Java Spring Boot + Zoho CRM SDK
✅ Step 1: Set Up Your Spring Boot Project
Start by creating a basic Spring Boot application using Spring Initializr (https://start.spring.io). Add dependencies like Spring Web, Spring Data JPA, and any database driver (e.g., MySQL or PostgreSQL).
spring init --dependencies=web,data-jpa mysql-springboot-zoho
✅ Step 2: Download and Configure Zoho CRM Java SDK
Go to Zoho Developer Portal and download the Java SDK. Add it to your project using Maven or Gradle.
For Maven:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.zoho.crm</groupId>
<artifactId>zcrmsdk</artifactId>
<version>5.0.0</version>
</dependency>
✅ Step 3: Authenticate with Zoho (OAuth 2.0)
Set up OAuth 2.0 credentials in Zoho API Console. Use the credentials to generate the access and refresh tokens. Configure the SDK with:
- Client ID & Secret
- Redirect URI
- Token file store (or database)
OAuthToken token = new OAuthToken("clientId", "clientSecret", "refreshToken", TokenType.REFRESH);
✅ Step 4: Create Repository and Service Layers
Use Spring Boot’s standard layered architecture:
- Controller: Accepts incoming HTTPS requests
- Service Layer: Business logic, dependency injection
- Repository: Extends
JpaRepository - Model: Your database entities
In the service layer, use the Zoho SDK to push/pull data to/from Zoho CRM modules (e.g., Leads, Contacts).
✅ Step 5: Call Zoho CRM APIs Using SDK
Example: To fetch all leads from Zoho:
ZCRMModule moduleIns = ZCRMModule.getInstance("Leads");
BulkAPIResponse response = moduleIns.getRecords();
List<ZCRMRecord> records = response.getData();
You can also create/update/delete records, log errors, and handle pagination directly.
✅ Step 6: Logging, Token Store, and Exception Handling
The SDK provides built-in components like:
LoggerSDKExceptionTokenStore(File or DB)UserSignature,RequestProxy,HeaderMap
This makes your app scalable and ready for multi-user access, clean logging, and secure authentication.
✅ Step 7: Test & Deploy
Test all endpoints (GET/POST) using tools like Postman or Swagger. Once everything is stable, deploy your app on cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Zoho Catalyst.
🎯 Real-World Benefits
With this setup, you save 100+ development hours by skipping custom API integrations. The SDK takes care of OAuth tokens, retries, headers, and payload formatting. Your team focuses only on business logic while Zoho handles the CRM backend.
📞 Need Help? Talk to Codroid Labs
If you’re looking to build a Java-based backend that integrates seamlessly with Zoho CRM, Codroid Labs is here to help. We specialize in Zoho CRM implementations, Java full-stack development, and custom SDK-based automation.
📱 Contact: +91 7838402682
🤝 Zoho Partner | Codroid Labs
